With pandemic concerns spurring the movement of customer interactions – both B2B and B2C – to digital channels, marketers are increasingly interested in technologies that collect data from those interactions, unify them, deliver insights and enable campaign orchestration.
A customer data platform, usually called a CDP, is a marketer-managed system designed to collect customer data from all sources, normalize it and build unique, unified profiles of each individual customer. The result is a persistent, unified customer database that shares data with other marketing technology systems.
The idea of a single view of the customer has been on marketers’ wish lists for years. But disruption caused by the global COVID-19 pandemic has raised interest in precisely the types of solutions that CDPs deliver, which includes that single-view of the customer. With pandemic concerns spurring the movement of customer interactions – both B2B and B2C – to digital channels, marketers are increasingly interested in technologies that collect data from those interactions, unify them, deliver insights and enable campaign orchestration.
What do customer data platforms (CDPs) do?
As the marketer appetite for CDPs has grown, existing companies with various backgrounds — from tag management to analytics to data management — have seen the opportunity and refashioned themselves in the CDP mold. Meanwhile, others have started up with the CDP category in mind from the start, and some well-established players have responded to market pressure and developed a CDP capability.
We support the CDP Institute’s definition of a “RealCDP,” which requires it be able to do the following five things:
- Ingest data from any source.
- Capture full detail of ingested data.
- Store ingested data indefinitely (subject to privacy constraints).
- Create unified profiles of identified individuals.
- Share data with any system that needs it.
Virtually all of the CDP vendors that meet that criteria provide the following core capabilities:
- Data management (collect, normalize and unify customer data in a persistent database),
often after IDs have been matched by other systems. - Features designed for use by the marketing organization and other departments, without the
aid of IT or data science resources. (Though some functions, like building connections to other
platforms and performing sophisticated data modeling, still require additional resources.) - Connections to and from all external systems on a vendor-neutral basis.
- Structured and unstructured data management.
- Online and offline data management.
CDP vendors differentiate by offering more advanced capabilities that include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Identity resolution to stitch customer data snippets from disparate sources.
- The number and breadth of robust pre-built connectors to other martech systems. The near-universal availability of APIs means connections are always possible (with more or less developer involvement), but offering pre-built, tested integrations adds value.
- User interface (UI). The vendors differ in the user-friendliness of their interfaces and the methods people use to do things like create segments, view profiles, etc.
- Analytics, including those powered by machine learning and artificial intelligence, that surface insights, enable journey mapping, audience segmentation and predictive modeling.
- Orchestration for personalized messaging, dynamic interactions and product/content recommendations.
- Compliance with vertical industry and international data regulations.
Now, let’s look at the key considerations involved in choosing a CDP.
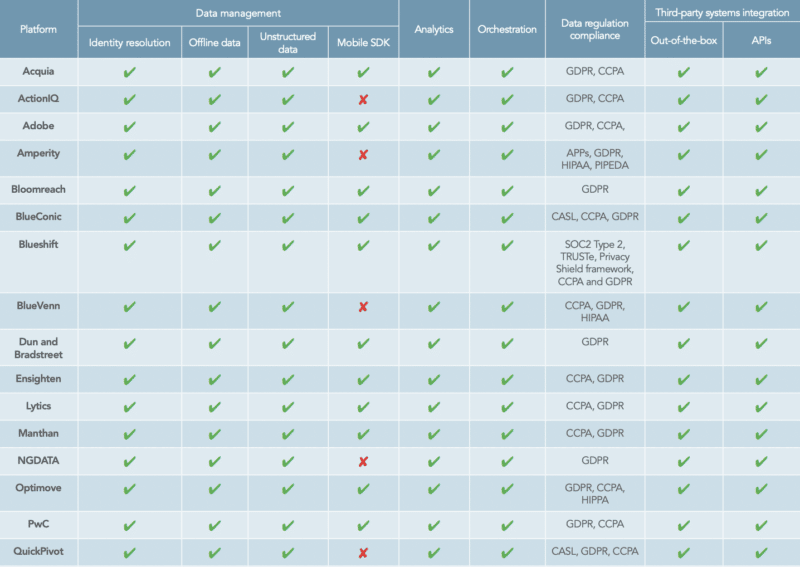
Data management
Data collection and maintenance is a core CDP function. All CDPs provide a central database that collects and integrates personally identifiable customer data across the enterprise.cFrom there, however, CDPs vary in their abilities to manage the following:
- Data ingestion capabilities: CDPs use various mechanisms to ingest the data that goes into the unified customer profile — mobile SDKs, APIs, Webhooks or built-in connectors to other platforms. Identity resolution: The platform “stitches” together customer data points, such as email addresses, phone numbers, first-party cookies and purchase data, from various channels matching them to create a single customer profile.
- Online/offline data: The platform leverages identity resolution or an identity graph to stitch together behaviors in order to create a unified profile.
- Data hygiene: The platform enables users to clean and standardize customer records.
- Structured/unstructured data: CDPs differ in their capabilities to manage unstructured data (i.e., social media feeds, product photos, barcodes), which may comprise up to 80% of all data by 2025, according to IDG.
The importance of each of these data management capabilities will depend on a particular organization’s business goals, and whether it has a significant mobile presence, direct mail budget or brick-and-mortar stores and/or agents.
Analytics
CDP vendors offer data analytics capabilities that can do some or all of the following: allow marketing end-users to define and create customer segments, track customers across channels and glean insights into customer interest and intent from customer behavior and trends. The specific tools provided can include predictive models, revenue attribution and journey mapping. To one extent or another, many of these capabilities may utilize machine learning
or artificial intelligence to surface insights about audiences and proactively offer suggestions about the best next step to move a prospect through their purchase journey.
Orchestration
A select group of CDPs provide campaign management and customer journey orchestration features that enable personalized messaging, dynamic web and email content recommendations, as well as campaigns that trigger targeted ads across multiple channels.
The CDP often automates the distribution of marketer-created customer segments on a user-defined schedule to external martech systems such as marketing automation platforms, email service providers (ESPs), or web content management systems for campaign execution.
For example, the CDP could deliver targeted content to a web visitor during a live interaction. To do this, the CDP must accept input about visitor behavior from the customer-facing system, find the customer profile within its database, select the appropriate content and send the results back to the customer-facing system. A CDP may also facilitate digital advertising through an audience API that sends customer lists from the CDP to systems (i.e., DMP, DSP, ad exchange) that will use them as advertising audiences.
Data regulation compliance
CDP vendors vary in the support they provide for compliance with the wide range of vertical market and international regulations that safeguard customer data privacy. Some build compliance features into their platforms, while others rely on outside systems. The European Union’s GDPR was implemented in May 2018 and impacts all U.S. marketers and data firms handling European data or serving customers in the EU. Brands marketing to Canadian consumers through email must also comply with the country’s CASL (Canada Anti-Spam
Legislation). Meanwhile, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) went into effect in January of 2020.
Marketers in the highly regulated healthcare market must follow HIPAA and HITECH regulations. In addition, all organizations that accept, process, store or transmit credit card information must maintain a secure environment that meets Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS), as well.
Third-party systems integration
CDPs streamline integration of customer data by providing out-of-the-box (or native) connectors for many martech systems, including CRMs, DMPs, marketing automation platforms, DSPs, and campaign analytics and testing tools. Most marketing organizations have assembled a marketing stack that contains many of these types of platforms. But integrating the data that resides in the martech ecosystem is a huge challenge — one that costs U.S. brands millions of dollars annually. The majority of CDPs profiled in this report also provide at least a basic API to enable custom integrations.
Explore platform capabilities from vendors like Blueconic, Tealium, Treasure Data and more in the full MarTech Intelligence Report on customer data platforms.
The benefits of using a CDP
Marketing executives today are in charge of dozens of martech applications to manage, analyze and act on a growing volume of first-party customer data. But despite increasing efficiency, the emerging martech ecosystem has created problems with data redundancy, accuracy and integration.
Automating customer data accuracy and integration through a CDP can provide numerous benefits to marketers and to other functions across the enterprise, though we’re focused on the marketing implications in this report.
These include the following:
Expanded enterprise collaboration. A CDP fosters cooperation among siloed groups because it gathers data from throughout the enterprise and supports customer interactions across many touchpoints. The unification of data allows enterprises to see how strategies for audience, customer experience and execution all fit together – and enables audience portability to ensure a more consistent, informed customer experience.
Improved data accessibility. A CDP is a centralized hub that collects and houses customer data from every corner of the enterprise. Pieces of data are normalized and stitched together to build unique, unified profiles of each individual customer. The result is a persistent customer database whose main purpose is to gather and share data more easily and efficiently across the organization
Streamlined systems integration. A CDP unifies data systems across the enterprise, from marketing and customer service, to call centers and payment systems. By creating a single “system of record” for first-party customer data, data redundancies and errors can be minimized, and data can flow more quickly into — and out of — marketing automation platforms, email service providers (ESPs), CRMs and other martech systems.
Increased marketing efficiency. A CDP unifies individual data with unique IDs that create more robust customer records. Many manual tasks are also automated by the CDP, allowing marketers to focus on the creative and analytical tasks they are trained for. The result is more accurate modeling, targeting and personalization in marketing campaigns, and more relevant customer experiences with the brand across channels.
Faster marketing velocity. In many cases, CDPs are “owned” by marketing, minimizing the need for IT or developer intervention to collect, analyze and act upon data. With control in marketers’ hands, the time to segment and build audiences, execute campaigns and analyze results significantly decreases. That said, engineers may still be needed to perform deep data analysis and facilitate integrations. This is especially true as CDPs extend beyond marketing and into sales and service functions.
Stronger regulatory compliance. A CDP creates greater internal control over customer data, streamlining data governance to comply with the many regulations now impacting brands worldwide. Marketers in the healthcare industry must comply with both HIPAA and HITECH regulations. Businesses that handle European data or serve customers in the EU must also comply with GDPR and those dealing with Californians must deal with CCPA
(California Consumer Privacy Act). The majority of CDP vendors are both ISO and SOC certified for best practices in handling personally identifiable information (PII).
This article is written by Pamela Parker and originally published here